
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents  Previous Section
Previous Section

This URL does not contain a session ID, so the application object creates a new session by performing the following steps:
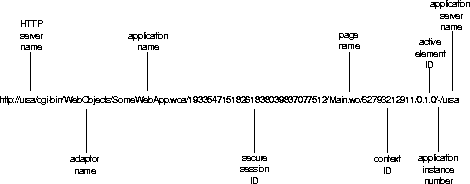
This URL contains all of the information necessary to restore the state of the existing session. The session ID comes right after the application name in the URL. Because sessions are designed to protect the data of one user's transactions from that of another, session IDs must not be easily predicted or faked. To this end, WebObjects uses randomly generated 32-digit integers as session IDs. (You can also override WOSession's sessionID method and implement another security scheme if you'd like.)
The application keeps existing, active sessions in the WOSessionStore object. The application object uses the session ID to retrieve the appropriate session from the session store (see Figure 22). The appropriate session object is then sent the awake message to prepare it for the request.
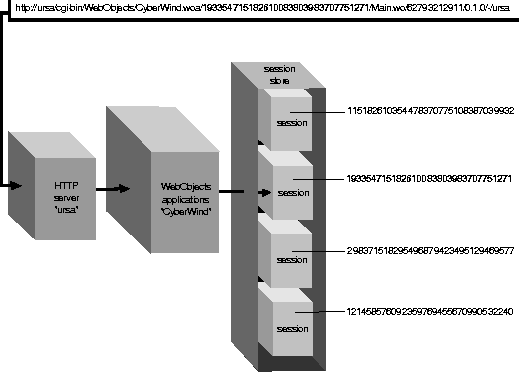
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents  Next Section
Next Section